ComparisonScaling Software Development - ZeroBlockers vs Waterfall: Which product development framework is better for you?
There is no one-size-fits-all framework for software development. Each framework covers different parts of the process in different ways. We have compiled an overview of the key features and approaches of the Waterfall framework and ZeroBlockers to help you select the best framework for you.
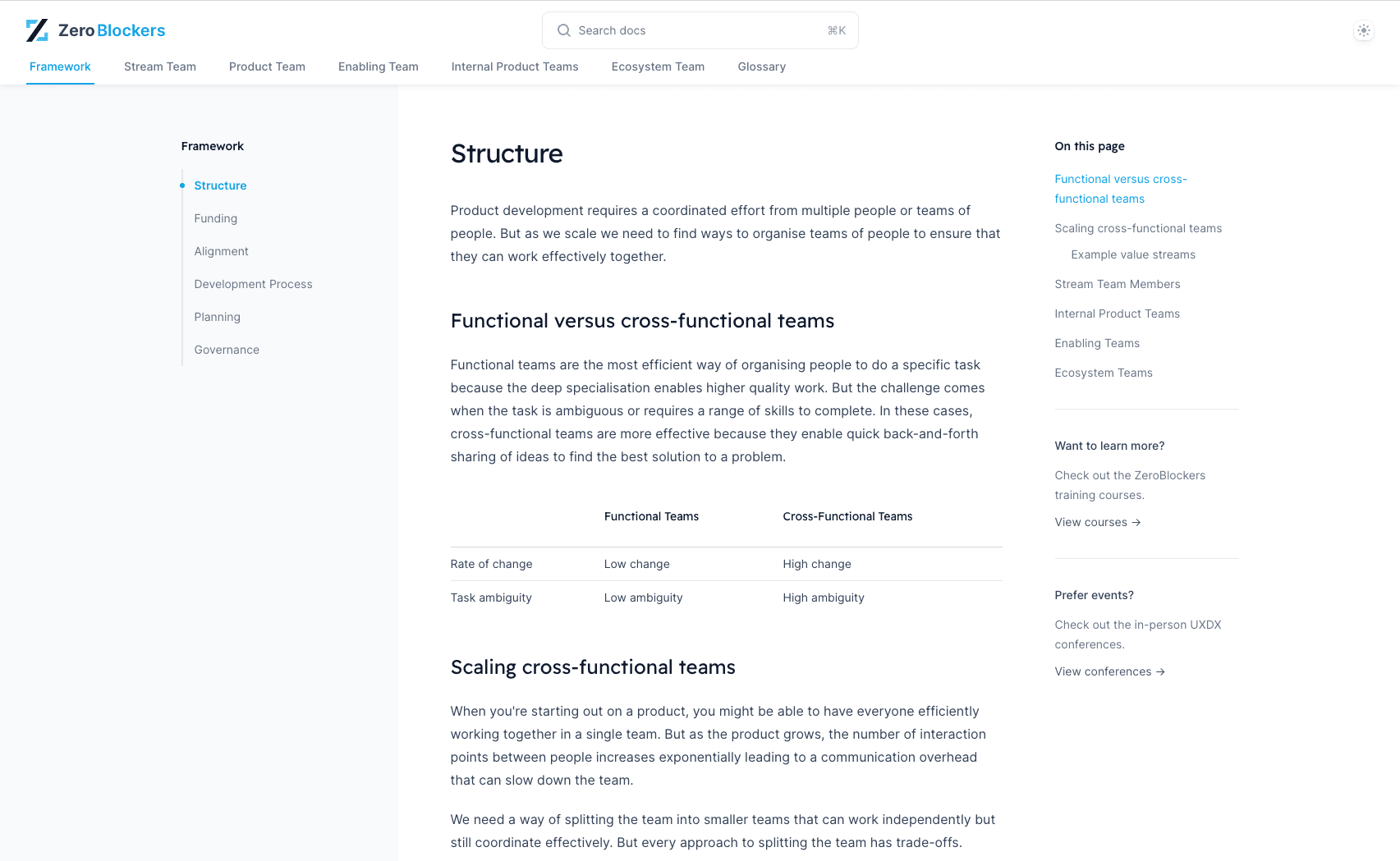
ZeroBlockers vs Waterfall: Overview
| Scroll | Idea Generation | Idea Evaluation | Business Case Creation | Business Case Approval | Plan | Analyse | Design | Develop | Test | Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waterfall | ||||||||||
| ZeroBlockers | Step Removed | Step Removed |
Feature comparison
ZeroBlockers
Effective products with empowered autonomous teams
Framework
- Process
The core way of working.
- Discover opportunities, design and evaluate solutions, then deliver in very small iterations.
- Planning
How teams prepare for the work to be done.
- Team conducts research, identifies opportunities, devises experiments and runs short experiments to evaluate solutions.
- Execution
How teams deliver on their plans.
- The team work cross-functionally together on all tasks, using a very small WIP to avoid context switching.
- Testing
How teams ensure quality.
- Guidelines for continuous automated unit and integration testing.
Waterfall
A linear and sequential approach to software development.
Framework
- Process
The core way of working.
- Distinct phases such as Planning, Analysis, Design, Build, Test, Deploy, Maintenance.
- Planning
How teams prepare for the work to be done.
- Detailed project plans, schedules, and resource allocations are established upfront, with a clear roadmap of the entire project.
- Execution
How teams deliver on their plans.
- Each phase is completed sequentially. Work is handed over from one function to the next after each phase.
- Testing
How teams ensure quality.
- Testing is a distinct phase that occurs after the completion of the build phase.
Core Differences
Framework
- Process
The core way of working.
- Iterate from idea to satisfied customers
versus
big-bang from solution to working software. - Planning
How teams prepare for the work to be done.
- Iterative planning
versus
big design up-front. - Execution
How teams deliver on their plans.
- Continuous synchronisation
versus
stage gate handoffs. - Testing
How teams ensure quality.
- Continuous testing and release
versus
testing at the end.
The principles behind the two frameworks are completely opposing. Waterfall assumes that the solution defined upfront is the best solution and that the team should focus on delivering it. It is more efficient to build a solution in one go rather than breaking it up into smaller pieces if you are confident that the solution is correct.
ZeroBlockers assumes that it is not possible to know how people will react to our products upfront so we need to identify the best solution through experimentation. We break up the solutions into small iterations so that we can get feedback quickly and iterate on the solution.
ZeroBlockers vs Waterfall: Approach
Feature comparison
ZeroBlockers
Effective products with empowered autonomous teams
Efficiency
- Lead Time
The time from when you identify an opportunity until the software is in place.
- Lead time as a core metric coupled with strategies on how to break up requirements into releasable iterations.
- Controlling complexity
Complexity and dependencies increase as companies scale.
- Dependencies and blockers need to be removed as they always slow down delivery.
- Reducing Code Conflicts
Code merge conflicts increase as more teams operate on the same code base.
- Each Stream team has a completely independent code base so code merge conflicts do not occur.
Waterfall
A linear and sequential approach to software development.
Efficiency
- Lead Time
The time from when you identify an opportunity until the software is in place.
- Bias towards larger projects so lead time can be very long.
- Controlling complexity
Complexity and dependencies increase as companies scale.
- Detailed upfront planning identifies dependencies and creates plans to mitigate them or factor overhead into plans.
- Reducing Code Conflicts
Code merge conflicts increase as more teams operate on the same code base.
- Waterfall does not have any opinions on merge conflicts.
Core Differences
Efficiency
- Lead Time
The time from when you identify an opportunity until the software is in place.
- Small, quick iterations
versus
large projects and slow lead time. - Controlling complexity
Complexity and dependencies increase as companies scale.
- Strategies for removing dependencies
versus
assumes dependencies can be managed. - Reducing Code Conflicts
Code merge conflicts increase as more teams operate on the same code base.
- Strategies for removing code conflicts
versus
no guidance for code conflicts.
Waterfall assumes that there is no value until the full solution is delivered. This means that teams are incentivised to build the full solution before releasing it.
In contrast, ZeroBlockers forces teams to release early and often by making it a core metric. The framework gives teams strategies for breaking down solutions into working iterations so that teams can achieve very short lead times and get the critical feedback required to improve their products.
The other core difference regarding efficiency is that Waterfall focuses on how a single team operates but often the biggest challenges are how teams work together. As companies scale the number of dependencies between teams increases and this slows down delivery. ZeroBlockers focuses on removing these dependencies.
Feature comparison
ZeroBlockers
Effective products with empowered autonomous teams
Effectiveness
- Solution Autonomy
Layers of sign off for solutions prevent teams from iterating quickly based on customer feedback.
- Teams decide on what features to build based on customer research and business objectives.
- Solution Validation
Most features fail to deliver the expected business outcomes. How can teams adapt as they deliver?
- Teams identify the assumptions behind their solutions and devise experiments to validate them before committing to building the feature.
- Accountability
What are the key KPIs that teams are measured on?
- Accountable for outcomes: The achievement of the Product Objectives.
Waterfall
A linear and sequential approach to software development.
Effectiveness
- Solution Autonomy
Layers of sign off for solutions prevent teams from iterating quickly based on customer feedback.
- Solutions are signed off in a business case and designs are completed upfront. Teams execute on the designs.
- Solution Validation
Most features fail to deliver the expected business outcomes. How can teams adapt as they deliver?
- User acceptance testing takes place at the end of the project.
- Accountability
What are the key KPIs that teams are measured on?
- Accountable for outputs. The delivery of the approved features within time and budget.
Core Differences
Effectiveness
- Solution Autonomy
Layers of sign off for solutions prevent teams from iterating quickly based on customer feedback.
- Empowered teams
versus
feature delivery teams. - Solution Validation
Most features fail to deliver the expected business outcomes. How can teams adapt as they deliver?
- Solutions validated by customers
versus
solutions verified by stakeholders. - Accountability
What are the key KPIs that teams are measured on?
- Measuring outcomes (impact of work)
versus
measuring outputs (scope, time and cost).
Waterfall assumes that it is possible for a business person to define the best solution upfront and that it is possible for the business to effectively communicate the solution in full to the team.
ZeroBlockers takes a completely different approach because the core principle is that you cannot know how customers will react to new features until they have them in their hands. It is not fair to ask a business person to specify the outcome of a feature because we don't know. We all have ideas that sound great but few of them work. Therefore solution evaluation and iteration are integral parts of the process. We empower teams to identify the best solutions and then hold them accountable for outcomes.
Feature comparison
ZeroBlockers
Effective products with empowered autonomous teams
Sustainability
- Technical Debt
Technical debt can make software delivery unsustainable unless it is continuously paid down.
- Teams own code and are responsible for maintaining its quality.
- Continuous Improvement
There are always improvements that can be made. How do we ensure that teams are always improving?
- Teams have a clear vision of what good looks like. Zero blockers from idea to software.
- Burnout Prevention
Team motivation is critical for ensuring that momentum is maintained.
- Giving people autonomy over the way they solve problems reduces burnout.
Waterfall
A linear and sequential approach to software development.
Sustainability
- Technical Debt
Technical debt can make software delivery unsustainable unless it is continuously paid down.
- Waterfall does not have any opinions on technical debt.
- Continuous Improvement
There are always improvements that can be made. How do we ensure that teams are always improving?
- Lessons learned are captured at the end of the project.
- Burnout Prevention
Team motivation is critical for ensuring that momentum is maintained.
- Upfront planning is expected to limit surprises and lead to a sustainable way of working.
Core Differences
Sustainability
- Technical Debt
Technical debt can make software delivery unsustainable unless it is continuously paid down.
- Ownership of code and maintenance
versus
no explicit guidance. - Continuous Improvement
There are always improvements that can be made. How do we ensure that teams are always improving?
- Teams decide on improvements
versus
PMO updates stage gate criteria. - Burnout Prevention
Team motivation is critical for ensuring that momentum is maintained.
- Tackle the cause of burnout
versus
no focus on burnout.
Shared code is subject to the tragedy of the commons. Each team has a tight deadline so they need to cut corners at the end. Waterfall assumes that you can plan around code dependencies but as companies scale the number of dependencies increases. You get cascading impacts of delays because every project is interdependent.
ZeroBlockers works on the principle that you cannot manage around dependencies - you have to remove them. Shared code and environments are two of the largest dependencies so we remove them by giving each team their own code base and environment.
Burnout isn't caused by challenging targets or high workloads. It is caused by being held to targets that you can't control such as an unrealistic deadline that was imposed on you. By giving teams autonomy over the way they achieve the product goals you are putting them in control. We can still set challenging stretch targets but, once teams can control how they achieve the targets, this can energise rather than cause burnout.
ZeroBlockers vs Waterfall: Team & Events
Feature comparison
ZeroBlockers
Effective products with empowered autonomous teams
Team Level
- Roles
The roles involved in creating the products.
- UX Researcher
Designer
Developers
Business SMEs as needed - Events
The key activities that teams perform while building the product.
- Ad-hoc
Customer Interviews
Ideation
Solution Evaluation
User Story Mapping
Daily
Retrospective
Weekly
Weekly Business Review
1-on1's
Waterfall
A linear and sequential approach to software development.
Team Level
- Roles
The roles involved in creating the products.
- Project Manager
Architect
Business Analyst
Development Team
QA - Events
The key activities that teams perform while building the product.
- Weekly
Status Report
Biweekly
Steering Committee
Ad-hoc
Stage Gate Reviews
Core Differences
Team Level
- Roles
The roles involved in creating the products.
- Skills to identify, evaluate and build solutions
versus
skills to build solutions. - Events
The key activities that teams perform while building the product.
- Researching, validating and building solutions
versus
building features
Waterfall is based on the principle that it is more efficient for specialists to focus on their area of expertise. By defining a clear process specialists can do their work and handover to the next specialist. This works exceptionally well when completing repetitive tasks such as on a manufacturing assembly line.
ZeroBlockers recognises that software development is a unique activity. We never build the same thing twice - you can copy and paste code! This means that each handoff is unique and context gets lost when handing over via documentation. The core principle is that it is more efficient to have cross-functional teams working from problem through to solution when you are working on unique problems.
ZeroBlockers vs Waterfall: Implementation
Feature comparison
ZeroBlockers
Effective products with empowered autonomous teams
Implementation
- Buy In
The people you need committed to ensure a successful roll-out.
- Considerable changes are required across the business so buy-in is required at a senior level in IT, marketing, customer service and more.
- Training
The training and certification required for a successful implementation.
- ZeroBlockers provides a range of training and certifications for each role.
- Community & Support
The support available for implementing the framework.
- Large and growing community with documentation and resources.
Waterfall
A linear and sequential approach to software development.
Implementation
- Buy In
The people you need committed to ensure a successful roll-out.
- Standard structure of IT departments.
- Training
The training and certification required for a successful implementation.
- A large array of training options for each role in the waterfall process including project management, architecture, and more.
- Community & Support
The support available for implementing the framework.
- There is a large and active community for each role.
Core Differences
Implementation
- Buy In
The people you need committed to ensure a successful roll-out.
- Whole business buy-in
versus
IT buy-in - Training
The training and certification required for a successful implementation.
- Similar between frameworks
- Community & Support
The support available for implementing the framework.
- Waterfall functions have larger communities
Waterfall is easier to implement because it is the standard way of working across most IT departments. It therefore requires fewer changes and has more support.
ZeroBlockers involves changes across the business - because software is integral to our products today - not something just tacked on. This means you need more buy-in to get started. But you can start small - one product, one value stream. With over 10 years of UXDX content and case studies, there is also a large body of resources to assist in the rollout of the framework. It might be tougher to implement but it will deliver better outcomes.